Waterjet and laser cutting technologies emerged in the 20th century as cutting devices typically used for manufacturing and industrial purposes and have come to be two of the most widely used techniques today. Although both technologies are capable of cutting material, a key distinguishing factor between the two technologies is laser cutting involves the use of a laser to vaporize material while waterjet cutting involves the use of a waterjet to cut material. Though both processes are highly versatile and can handle a wide range of materials, they each have advantages and disadvantages. This post will delve into the differences and the pros and cons of waterjet vs laser cutting, and the applications each cutting technology is ideal for.
The History of Waterjet Cutting
A waterjet cutter is a mechanical tool that has the capability of cutting various types of materials. Waterjets were first used in the mid-1800s by coal miners in hydraulic mining. Due to the success of this application, advancements in waterjet cutting technology continued to rise until waterjet cutting using narrow jets of water was introduced as a cutting device in the 1930s. Early applications functioned at a lower pressure and were limited to soft materials. It was not until the 1970s that the durability of the waterjet nozzle was improved when a waterjet nozzle containing an orifice as tiny as 0.002 inches, and reaching pressures up to 70,000 psi, was created. The development of the high-pressure fluid intensifier in 1973 set the groundwork for the commercial viability of waterjets, which was further refined in 1976. Waterjet cutting was brought into the manufacturing world when high-pressure pump research was combined with waterjet nozzle research by Flow Industries.
How Waterjet Cutting Works
A waterjet cutter contains the X (left and right), Y (back and forth) and optionally Z (up and down) axes, cutting head tilt axes, as well as a material catcher tank. Due to technological advancements, 5-axis water jet cutting has recently become available, which typically includes the addition of an A-axis and C-axis. The waterjet control system includes the programming software, operator interface, drive motors, and position and velocity feedback system. A waterjet generates pressure using an ultrahigh-pressure system, containing a pump, cutting head, and plumbing capable of generating pressure up to 94,000 psi. An intensifier pump and a direct drive pump are two types of pumps used to generate high pressure that is converted into velocity through a tiny jewel orifice.
Waterjet Types
The two types of waterjet cutting systems are pure waterjet and abrasive waterjet. Waterjet cutters use either a jet of pure water without added abrasives that function at high pressure or a combination of an abrasive substance (such as garnet) and water, which increases the cutting power. Pure waterjet is typically used on softer materials including paper, rubber, foam, wood, and carpet, while abrasive waterjets can cut much harder materials including stone, ceramic, glass, and metal.
What Is Waterjet Cutting Used For?
Waterjet cutting services are often used by mining and aerospace industries for cutting, shaping, and reaming, and in the fabrication of machine parts. Waterjet cutting is a popular cutting method when certain materials are being used such as aluminum and plastic, which would otherwise be sensitive to the high temperatures they would be exposed to through alternate cutting methods.
Pros of Waterjet Cutting
Water jet cutters are extremely accurate and can create intricate cuts or 3-D shapes in a wide variety of materials without producing any heat damage to the edges and surfaces of workpieces. This assures that pieces are uncompromised. Waterjet cutters cut nearly any type of material including tough materials such as bullet-proof glass, metals, stone, as well as materials with uneven surfaces. No hazardous waste is created by waterjet cutters. There are however some disadvantages as well, which we will mention below.
Disadvantages of Waterjet Cutting
Though waterjet cutters can cut virtually any type of material, they often take longer to cut materials than traditional cutters. Low-quality waterjet orifices are known to break down, which could result in a loss of time and productivity and disrupt the cutting process. Greater material thickness results in less accuracy since the thicker the material, the further the stream is from the nozzle, resulting in an inconsistent impact and an uneven cutting accuracy from top to bottom.
The History of Laser Cutting
During the 1960s, the first laser cutting machine was invented, paving the way for further developments. At the start of the 1970s, laser cutting technology was utilized by aerospace industries to cut titanium. During the start of the 1990s, laser cutting started to flourish and advance. Laser cutting today is a very popular process for manufacturing and industrial cutting and is used by various industries including engineering, architecture, construction, medical, and marine.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting is a CNC (computer numerical control) cutting process that is capable of cutting through materials with the aid of a high-power laser directed through optics. The process involves a laser beam that is focused onto the workpiece and directing it at the material through either a cutting, vaporizing, melting, burning, or blowing away method, using a jet of gas. This results in a high-quality surface finish. A CNC laser uses a process involving a motion control system to follow a CNC or a G-code of the pattern being cut onto the selected material.
Types of Laser Cutters
Manufacturers use three types of laser cutters. These include:
CO2 Laser Cutters
CO2 gas lasers are largely used in manufacturing since they are low cost and efficient and can pierce thicker materials than fiber cutters with similar power output and are directed at a wavelength of 10.6 mm. CO2 lasers use a laser that is comprised of mostly carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium and are pumped using electric discharge. These lasers are commonly used for working with paper or wood, as well as polymethylmethacrylate.
Fiber Laser Cutters
These lasers use a solid gain medium, use fiber optics, and are up to 3 times more energy-saving than cutters that are gas-based. Fiber lasers are easier to maintain since they do not contain any moving parts such as fans for gas circulation. An advantage of fiber-based lasers is that they can cut reflective materials and thin sheets at a higher speed than carbon gas-based lasers while functioning at the same power. For laser engraving metal, a fiber laser cutter is an ideal choice. They are capable of marking brass, various types of aluminum, copper, nickel-plated metals, and laser engraving steel.
Nd:YAG/Nd:YVO Lasers
YVO, or YAG, are crystal laser cutting processes that have a higher intensity and smaller wavelengths. These laser cutters have exceptionally high cutting power and the capacity to cut through stronger and thicker materials than other types of cutters, though they are more expensive to operate since they wear out quicker due to their higher concentration. These lasers are used with metals and non-metals, as well as plastics.
The Benefits of Laser Cutting
Due to its high precision, laser-cut parts require minimal finishing. Laser cutting is the most widely used application in various industries due to its ability to both cut and engrave materials, its material versatility, precision, and cost-effectiveness, since it is more affordable than waterjet cutting.
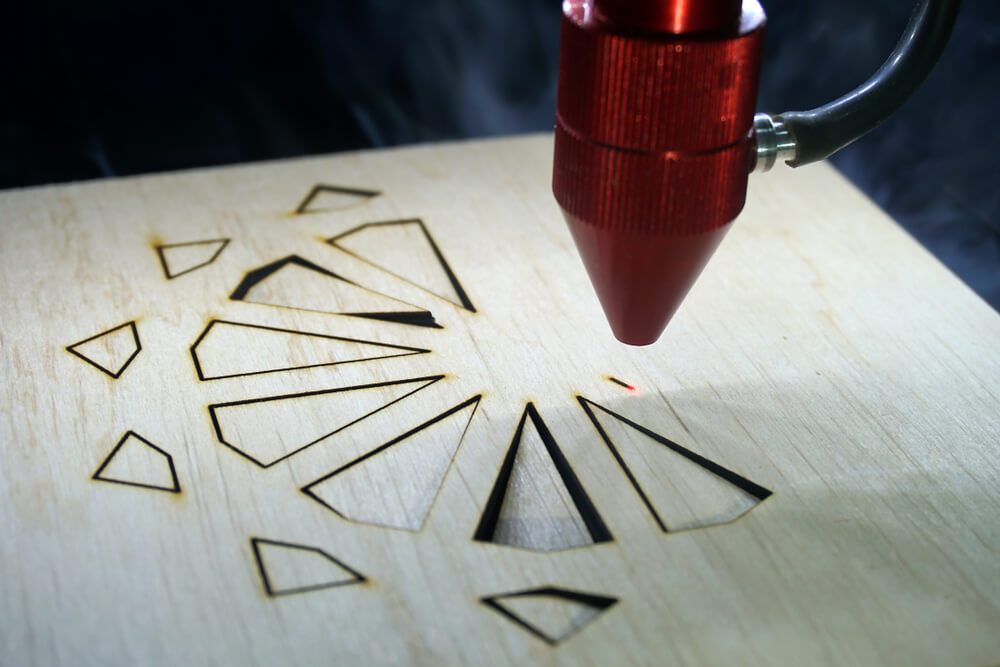

Disadvantages of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is often not very suitable for cutting very thick metal parts. Another downside is that material melts during this thermal cutting method, which can result in dangerous fumes and gases being emitted.
Similarities and Differences Between Waterjet Cutting and Laser Cutting
Both waterjet cutting and CNC laser cutting processes are highly versatile and offer a high rate of accuracy and precision. They produce minimal waste, offer quick delivery, and are high-quality due to advanced software and superior equipment. They both contain a small kerf width enabling them to create thin cuts and intricate shapes with fine details and exceptional precision. Both processes are ideal for a wide number of industries including the aerospace, architecture, automotive, manufacturing, medical science, and power industries.
The differences between waterjet cutting and laser cutting lie in their results, applications, and methods, including:
Waterjet cutting is generally the first choice when working with thicker and harder materials due to its high-pressure capacity. On the other hand, laser cutting is generally faster than waterjet cutting and offers a higher rate of precision, reaching tolerances of +/-0.005″ compared to waterjet cutting, which normally has a tolerance of +/- 0.01.” Laser cutting is the more cost-efficient option and is capable of cutting parts faster than waterjet cutting. In addition, a laser cutting machine is capable of cutting as well as engraving material; a waterjet only allows cutting.
Which technique is right for your application?
If you cannot decide whether waterjet cutting or laser cutting is the ideal application for you, eMachineShop can help discern the more appropriate technique to use, depending on factors including material thickness, the type of material being used, and whether you require engraving and higher precision. By considering the above-mentioned factors, you can assure that you choose the appropriate technology based on your requirements.