CNC Machining Services
On-demand CNC machining for custom metal and plastic machined parts, with fast online quoting, ordering and turnover time.
Learn more about our machining capabilities below or upload your design for a fast quote.
- 50+ Materials.
- FREE Shipping in the USA.
- 100% Quality Guaranteed.

Machining services
eMachineShop offers the highest quality CNC machined parts with tight tolerances from a wide variety of materials. Our advanced CNC machinery, including CNC mills and lathes, and experienced machinists enable us to manufacture virtually any part, regardless of its complexity. Our custom CNC manufacturing capabilities include:

CNC Milling
Mills use rotating tools to cut material into almost any 3D shape. CNC Mills can work with tight tolerances.

CNC Turning
CNC Lathes feed cutting tools into rotating material. Turning is mainly used to produce precise, cylindrical parts.
Get Your Custom Parts Machined to Perfection: Your Satisfaction is Our Top Priority!
eMachineShop offers instant quotes for your custom parts. Our customer service team will work with you to ensure your design specs are met. Order your part easily by following these steps:
-
Create or Upload your CAD file – Design your parts using our free CAD or upload your CAD files, PDF drawings, or images.
-
Configure your part – Select from over 50+ materials and surface finishes. Enter quantity, address and any special comments to the machinist.
-
Receive a quote – Get a quote for your design (instantly via our CAD).
-
Order your parts – Place your order and receive your quality CNC parts!

What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process in which computer software is used to control the movement and operation of lathes, mills, 3D printers and many other manufacturing machines. CNC machining makes precision parts with simple or complex shapes by automating the process of cutting metals, plastics, and other solid materials.
In CNC machining, a computer program written in the language G-code, is used to control all aspects of the machine. The G-code tells the machine what to do at each step, including motions, speeds and feed rates. The G-code is typically created using computer-aid-manufacturing (CAM) software which works from CAD software. The G-code is uploaded to the machine for processing.
CNC machining advantages over other processes
CNC machining allows for much faster setup times as compared to many other manufacturing processes such as forging, stamping, casting, and injection molding. The versatility of CNC machines means, depending on the complexity of the part and setup, the machine can be set up for a new part in less than an hour in some cases. Forging and casting parts require expensive tooling and long lead and changeover times. Similar and often better tolerances can be achieved with the use of CNC machines without the expensive initial costs for custom tooling. This advantage makes CNC machines cost effective for prototyping and small production runs, while still capable of doing large quantity runs.

Additional advantages include:
- Versatility – a wide range of parts can be made on the same machine
- Custom parts can be made without the need for custom tooling
- Shorter lead times required for parts
- Low initial setup costs
- The ability to run a machine autonomously allows for “lights out” manufacturing, reducing the need for an operator
- CNC machines can produce parts with higher levels of precision
- Wide variety of materials that can be used
Custom Machining – Applications

Custom CNC machining is used in a variety of industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, consumer products, scientific instruments, electronic devices and many other uses and applications. CNC manufacturing services help engineers and machinists design and produce unique models that offer pragmatic parts and solutions for consumer and industrial needs such as engine components, housing brackets, and even medical prosthetics. CNC machining can produce complex shapes accurately which would be challenging and time consuming to manufacture using manual machining methods. Since CNC machining works conjointly with CAD files it is ideal for custom machining parts and prototypes. As a result, CNC machining has achievable applications for both commercial businesses and hobbyists alike for low and high volume production runs.
How does CNC machining work?
Raw material, often in block form, is first mounted in the machine on a “workholding device” such as a vise, which holds the material that is being machined.
The CNC machine reads the G-code program to move cutting tools in a predetermined sequence. The cutting tools move along the X, Y, and Z axes, and can also rotate around their own axis. In more advanced machines there are even more axes of movement. This allows the CNC machine to produce parts with complex geometries and high levels of precision.
During the machining process, the machine tools remove material from the workpiece by cutting, drilling, or milling it. As the material is removed, the workholding device moves the workpiece to the correct position for the next machining operation, as specified by the G-code. This process is repeated until the desired part has been fully machined.

Upload your file
for a fast quote
Get a Quote
No CAD file?
Draw it easily with our CAD
GET FREE CAD
Types of CNC Machining
There are several different types of CNC machining, each of which is suitable for different applications and materials.
The most popular types of CNC machining services are:
- Milling is a type of CNC machining that involves the use of a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece.
- Turning is a type of CNC machining that involves the use of a lathe to shape a workpiece by rotating the raw material and applying a non-rotating cutting tool. Turning is usually used to produce cylindrical parts such as shafts and more complex shapes like a chess pawn.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) is a type of CNC machining that uses electrical discharges to cut and shape conductive materials such as metals. EDM is often used to produce parts with sharp inside corners that are not practical using other methods.
- Routing is another CNC process that is similar to milling but often restricted to simpler 2D shapes. It uses a rotating cutter to cut 2D shapes often from software materials like wood and plastics. However CNC routing can also be used to shape stone and other hard materials.
Comparison to manual machining
CNC machining and manual machining are similar in that they both involve the use of machine tools to cut and shape materials.
However, there are several differences:
- CNC is generally more precise and accurate than manual machining because CNC machining uses computers that are able to follow instructions accurately without errors.
- Machines that use a CNC process are typically faster than manual machining, as the machine tools are able to work continuously. This allows for the production of many parts in a short period of time.
- CNC machining is able to produce more complex parts than manual machining, as the machine tools are able to move along a variety of axes and can be programmed to follow complex paths.
- Most CNC machines are more costly but the higher upfront cost is often offset by the increased efficiency and precision of CNC machining, which can result in lower production costs.
Design specifications for machined parts

When designing custom parts for CNC machining services, there are many factors to keep in mind. It is important to understand the capabilities and limitations of CNC machining processes, such as mill and lathe machining, in order to create a design that can be practically machined.
Here are some design tips for parts that will be CNC machined:
- Complex shapes and features may be difficult or time consuming to machine, so it is generally best to keep the design as simple as possible.
- Sharp corners are often difficult to machine. Rounded corners or filets are recommended.
- Deep narrow pockets may be difficult to machine, as the tool may not be able to reach the bottom of the pocket and removal of chips can be an issue. Try to use shallower and wider pockets.
- Thin walls can flex during machining. Try to maintain a reasonable wall thickness to ensure that the part is strong enough to withstand the machining process.
- Tolerances are the allowable variations in the size and shape of a part. It is important to use appropriate tolerances for CNC machining, as overly tight tolerances may be difficult to achieve and may result in increased production costs.
- Tolerances are affected by the raw material. In general, metal machining services offer tighter tolerances, whereas plastic machining services offer slightly looser tolerances in comparison.
Cost reduction tips for CNC machining parts
There are a few things you can try to reduce the cost of CNC parts:
- Consider using a less expensive material. Different materials have different price points, and switching to a less expensive material could help reduce the overall cost of your parts.
- Some CNC machining processes are faster and more efficient than others, which can result in lower production costs.
- Most suppliers have lower costs as the order quantity goes up, so if you’re able to order a larger quantity of parts at once, you will likely get a better price. This is because setup costs must be amortized.
- Sometimes small changes to the design of a part can significantly reduce the cost of production.
- For small quantities, it may be more cost-effective to use 3D printing.


CNC Machining Design Guide
Using the latest in CNC machining technologies, eMachineShop can help you reduce the time and cost of machining prototypes and production runs. Learn how to streamline your next project by optimizing material, complexity, speed, cost and other factors.
Welcome to eMachineShop CAD
If your browser does not open a new tab automatically,
click here to open eMachineShop Browser CAD
Materials that can be machined

CNC machining can be used to machine various types of materials. CNC metal machining can be used for materials such as, aluminum, brass, copper, stainless, titanium, steel as well as many other metals. CNC plastic machining can be used for plastics materials such as acrylic, polycarbonate, teflon, ABS, etc. Some CNC machines are designed to handle more exotic materials such as Inconel or titanium machining, while others may be limited to machining softer materials such as brass or aluminum. Although CNC machining can be applied to both metal and plastic raw materials, the achievable tolerances differ for each material, with metals typically having tighter tolerance capabilities compared to plastic or other materials. When designing for CNC machining, it is important to consider the relationship between the material composition and properties to its intended functionality, as some materials are not suited for certain applications or environments.
Most popular CNC machining materials
How are CNC machines programmed?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are programmed using a specialized programming language called G-code. G-code is a standardized programming language that tells the CNC machine where to move the cutting tool, how fast to move it, and what path to follow.
To program a CNC machine, the programmer will typically start by creating a 3D model of the part they want to produce using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The programmer will then use CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software to generate the G-code instructions based on the 3D model and the specific tool paths required to machine the part.
Once the G-code has been generated, it can be loaded into the CNC machine’s controller and the machine will follow the instructions to produce the part.

CNC machine accuracy
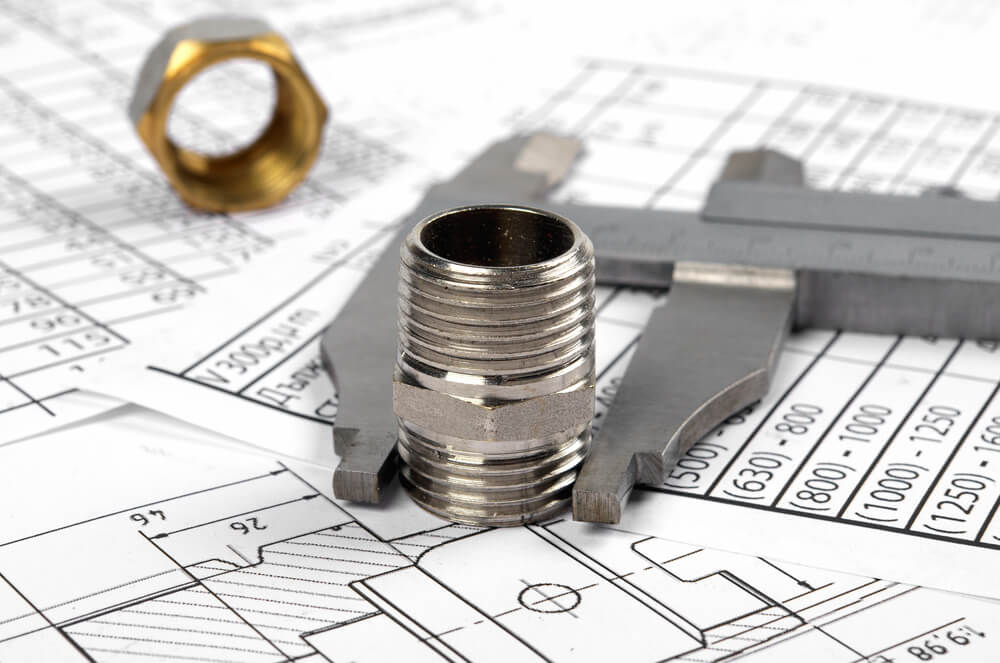
The accuracy of a CNC machine depends on a number of factors, including the quality of the machine itself, the skill of the operator, and the design of the parts being produced. In general, CNC machines are capable of producing parts with very high levels of accuracy, but the actual level of accuracy will depend on the specific machine and the particular application.
Most CNC machines are designed to be accurate to within a few thousandths of an inch (0.001 inches). However, some high-precision CNC machines are capable of achieving accuracies of a few ten-thousandths of an inch (0.0001 inches) or even better.
Even the best CNC machines are limited to the tools and fixtures being used and the quality of the raw materials being machined.
Tooling
CNC machines have a large variety in the types of applicable tooling. This offers increased accuracy and manufacturing efficiency. By being able to switch tooling and do multiple machining processes on the same machine and in the same fixture, it reduces variability in feature location from moving the part to a new machine or setup. For example, you can surface mill, slot mill, and drill and ream holes all while having the part in the same fixture and run using the same program. This also means the amount of labor required for each part can be minimized. The fewer hands and stations that the part needs to be moved to will decrease the labor required for each part. The ability to use many types of tools, allows a multitude of different materials that can be machined on the same machine.